AN UNCOMMON TRIAD: SOLITARY FIBROUS TUMOR, DOEGE-POTTER AND BAMBERGER-PIERRE-MARIE SYNDROMES
Keywords:
Solitary Fibrous Tumor, Pleural; Osteoarthropathy secondary hypertrophic; Hypoglycemia; Thoracic surgery.Abstract
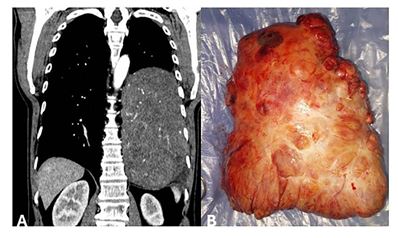
The solitary fibrous tumor (SFT) represents an uncommon mesenchymal neoplasm, typically exhibiting benign behavior. It primarily originates from the serosal membranes, with the potential for development across diverse anatomical locations. In rare instances, it can manifest concurrently with paraneoplastic syndromes. We present the case of a male patient with a pleural SFT, diagnosed incidentally via imaging studies, who presented clinically with two simultaneous paraneoplastic syndromes: Doege-Potter syndrome and Pierre-Marie-Bamberger syndrome. The diagnosis was confirmed through histopathological analysis and immunohistochemical techniques. Complete surgical resection was performed without complications, and the patient demonstrated favorable clinical evolution. This article reviews the clinical, diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic characteristics of this entity.